- Vishakha Sadhwani
- Posts
- AI Engineer Learning Path (For Developers)
AI Engineer Learning Path (For Developers)
A clear role breakdown, skill map, resources and certification path.
Hi Inner Circle,
Today we are talking about AI Engineers.
There are two common learning paths you’ll see for this role:
Developer focused (discussed today)
Data Scientist–focused (whole different flavor of AI 😄)
~ not part of our series but can dive into it if there’s interest.!
Alright, without wasting any time, let’s dive straight into our role.
If Cloud Engineers build systems and ML Engineers build models, AI Engineers bring intelligence into real applications.
This is an applied AI role.
AI Engineers don’t train models from scratch ~ they build systems around them.
They connect LLMs to applications, stitching together APIs, vector databases, and end-user workflows.
This role powers ChatGPT-like apps, copilots, agents, automations, and next-gen AI features.
In practice, AI Engineers work across:
→ LLM APIs
→ Embeddings and vector databases
→ RAG pipelines
→ Agents and orchestration frameworks
→ Prompt design, evaluation, and production deployment
Most people start at an Associate AI Engineer level (1–3 years of experience), then grow into Gen AI Engineer, Senior AI Engineer, and eventually Staff or Principal AI Engineer roles as they take ownership of larger systems and platforms.
Their job is simple to describe, but hard to execute:
Take a model → turn it into a real product → make it useful, reliable, and scalable.
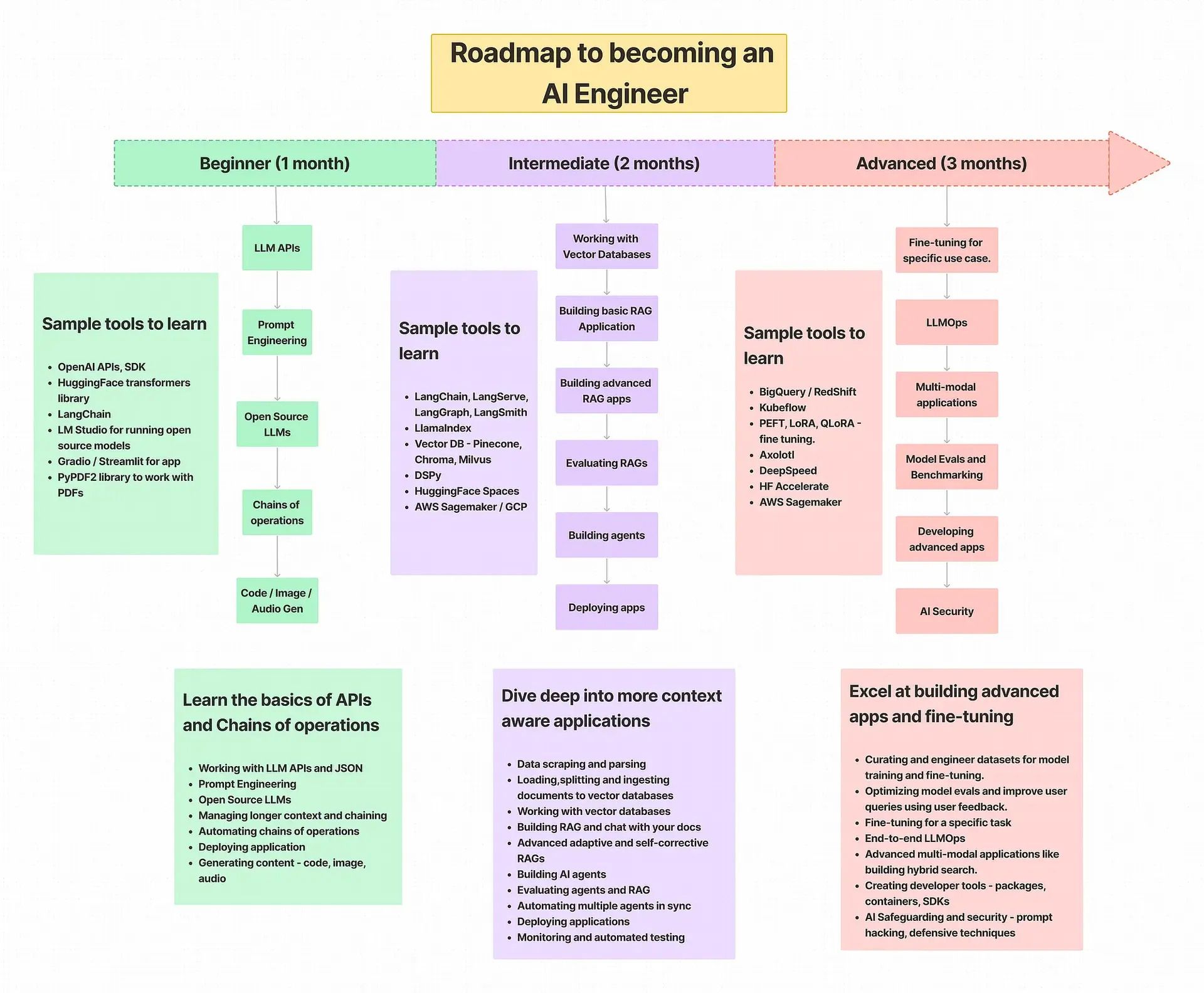
Image Credits - Harshit Tyagi
AI Engineer (Developer Focused) ~ The 5-Level Path
Before that ~ Start with Basic Foundations
→ Python fundamentals (functions, classes, async, testing)
→ API basics: requests, JSON, REST
→ Data formats: text, embeddings, vectors
→ Software engineering principles: modular design, logging, error handling
→ Prompt engineering basics: system prompts, zero-shot/one-shot/few-shot
→ Understanding LLM limitations: hallucination, context windows, safety
Level 1: Working with the OpenAI API (Your First AI Application)
Learn how LLMs plug into applications via APIs.
Core skills:
→ Making API calls with Python
→ Understanding model parameters (temperature, tokens, roles)
→ Zero-shot, one-shot, few-shot prompting
→ Building structured responses
→ Cost estimation & token budgeting
You should be able to:
Build text generation, summarization, classification, sentiment analysis, and simple chatbot flows with the OpenAI API.
Tools/Services:
OpenAI API • Anthropic API • Gemini API
Level 2: Prompt Engineering & AI Interaction Design
This is where you learn to control an LLM.
Focus:
→ Writing system messages
→ Designing prompt templates
→ Guardrails & constraints
→ Multi-turn conversations
→ Providing examples
→ Handling ambiguity
You should be able to:
Structure conversations, enforce behavior, prevent drift, and shape model outputs for real apps.
Level 3: Embeddings, Vector Databases & Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
To build search, chat-with-your-data, and contextual AI apps, you need embeddings.
Concepts:
→ What embeddings are: Numerical representations of text that capture meaning, so similar content ends up closer together.
→ How to generate them via OpenAI API: Use the embeddings endpoint to convert text into vectors with a single API call.
→ Storing & retrieving them efficiently: Save embeddings in a vector database to enable fast lookup at scale.
→ Similarity search: Find the most relevant content by comparing vector distances instead of keywords.
→ Chunking & indexing strategies: Break large documents into smaller pieces and index them to improve search accuracy and performance.
Tools:
Pinecone • Weaviate • ChromaDB
LangChain Embeddings • OpenAI Embeddings API
You should be able to:
Build a simple RAG pipeline and integrate it into your app.
Level 4: AI Frameworks, Agents & LLMOps Concepts
This is where AI apps grow from scripts → to real systems.
Focus areas:
→ LangChain: chains, tools, agents, memory
→ LLamaIndex: document ingestion, query engine
→ Workflow orchestration
→ Tool-calling & function-calling
→ Evaluation of LLM outputs
→ Monitoring, logging, fallback strategies
LLMOps Concepts:
→ Data pipelines for AI apps: Move, clean, and prepare data so AI features always get the right context.
→ Versioning prompts & models: Track changes to prompts and models so updates are reproducible and reversible.
→ Latency optimization: Reduce response time by caching, streaming outputs, and choosing the right model sizes.
→ Cost control: Manage token usage, model selection, and request frequency to keep AI spend predictable.
→ Observability for AI systems: Monitor outputs, errors, latency, and drift to understand how AI behaves in production.
You should be able to:
Build an AI agent that can search, call tools, retrieve data, and complete a task end-to-end.
Level 5: Building Full AI Applications & Production Deployment
Advanced AI engineering ~ turning prototypes into production-grade apps.
Focus:
→ Async architectures: Handle multiple AI requests concurrently without blocking your application.
→ API endpoints for AI features: Expose AI capabilities through well-defined REST or streaming APIs.
→ Secure inference (auth, rate limits): Protect AI endpoints with authentication, authorization, and usage limits.
→ Deploying RAG pipelines: Run retrieval and generation workflows reliably in production environments.
→ Stream responses: Send partial outputs in real time to improve user experience.
→ Handling scaling (vLLM, Triton optional): Scale inference efficiently by batching requests and managing GPU utilization.
You should be able to:
Deploy an AI-powered application using FastAPI / Flask + a vector database + an LLM provider.
Tools:
FastAPI • LangServe • Hugging Face Hub • Cloud Run • Vercel • Render • Railway
Resources
Beginner → Intermediate (AI Engineer Foundations)
Great starting point for understanding AI concepts, APIs, and practical usage.
(Includes courses on LLMs, RAG, prompt engineering, and production patterns)
Highly recommended for applied LLM development.
Framework & Platform-Specific (Developer-Focused)
Covers chains, agents, tools, RAG pipelines, and real-world LLM app patterns.
OpenAI Developer Learning Path
(For now, OpenAI’s official docs + examples are the best preparation)
Certifications:
Projects You Can Build
Quick Tip:
The fastest way to learn AI engineering is:
API → prompts → embeddings → vector DB → LangChain → real app.
Your Takeaway
AI Engineers don’t need to train foundation models.
They need to understand them deeply enough to build intelligent applications around them.
So you know the drill - start small. Build consistently.
Your best learning comes from shipping real AI apps.
You got this!
– V
This newsletter you couldn’t wait to open? It runs on beehiiv — the absolute best platform for email newsletters.
Our editor makes your content look like Picasso in the inbox. Your website? Beautiful and ready to capture subscribers on day one.
And when it’s time to monetize, you don’t need to duct-tape a dozen tools together. Paid subscriptions, referrals, and a (super easy-to-use) global ad network — it’s all built in.
beehiiv isn’t just the best choice. It’s the only choice that makes sense.

